Unlock Your Brain’s Secrets: Nervous System Worksheet – 1 Neuron, CNS, PNS, Synapse (Download Now!)
Meta Title: Nervous System Explained: Neuron, CNS, PNS & Synapse
Meta Description: Demystify the nervous system! Learn about neurons, CNS, PNS, and synapses. Includes a free worksheet to test your knowledge. Download now!
Introduction:
Ever wondered how your brain controls everything from breathing to complex thoughts? The answer lies within your intricate nervous system. This amazing network is responsible for receiving, processing, and responding to information from the world around you. Understanding the basics – the neuron, the Central Nervous System (CNS), the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), and the synapse – is the first step to unlocking the secrets of your brain. This article will break down these complex topics into digestible chunks, equipping you with the knowledge to understand how your body works. To further solidify your understanding, we’ve included a helpful nervous system worksheet you can download and use to test your knowledge! [Link to Worksheet - hypothetical download]
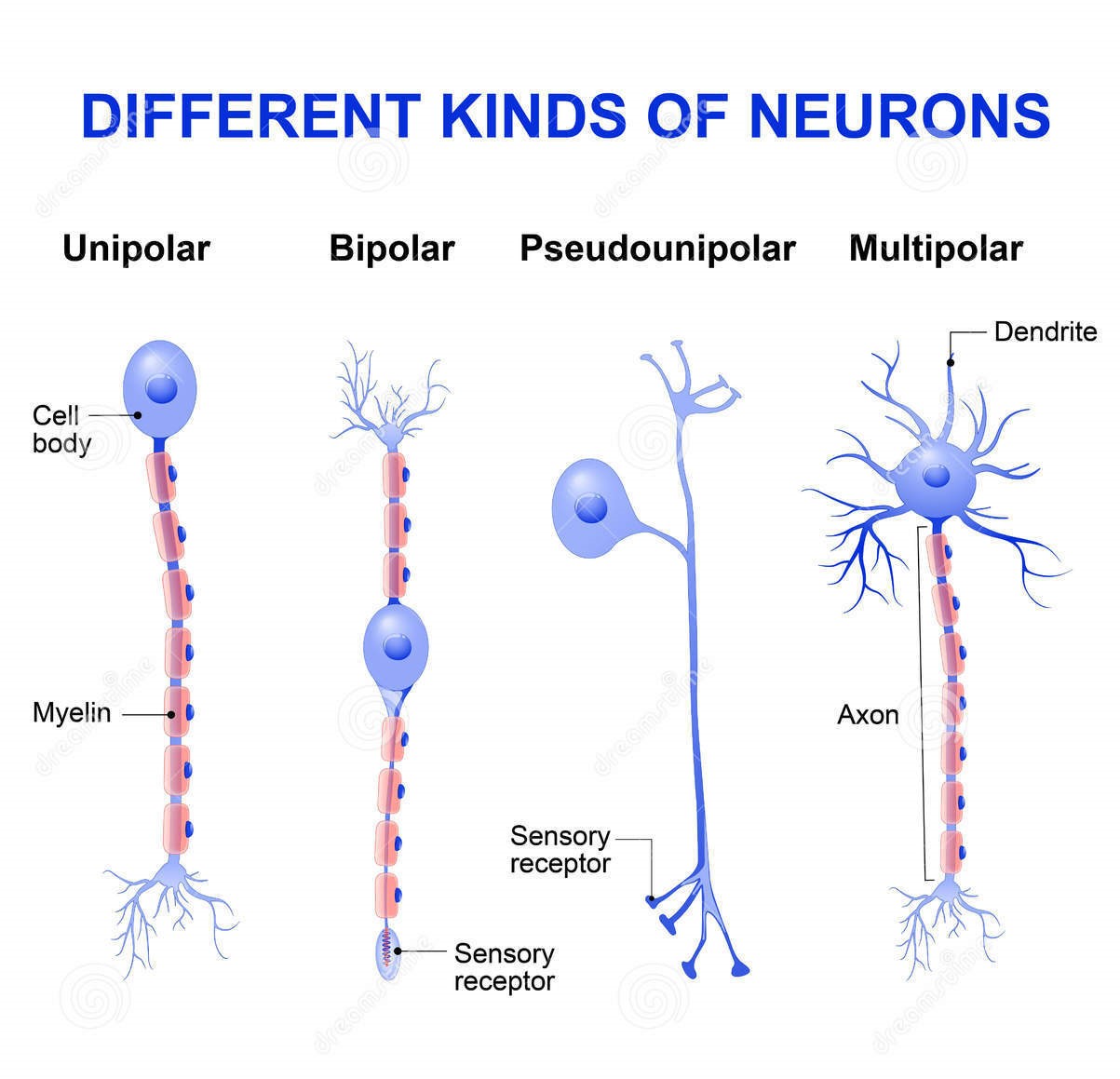
The Building Block: Understanding the Neuron
The fundamental unit of the nervous system is the neuron, also known as a nerve cell. These specialized cells are designed to transmit information throughout the body. Think of them as tiny messengers carrying electrical and chemical signals.
Key Parts of a Neuron:
- Cell Body (Soma): This is the neuron’s control center, containing the nucleus and other essential organelles.
- Dendrites: These branching extensions receive signals from other neurons. Think of them as antennas, collecting information.
- Axon: A long, slender projection that transmits signals away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
- Myelin Sheath: A fatty substance that insulates the axon, speeding up signal transmission. (Think of it like insulation on a wire).
- Axon Terminals: The end of the axon, where the signal is transmitted to the next neuron or target cell.
The neuron works by generating an electrical impulse called an action potential. This signal travels down the axon, allowing for rapid communication across the nervous system.
The Central Nervous System (CNS): The Control Center
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is the body’s command center. It’s composed of the brain and the spinal cord.
- The Brain: The brain is responsible for a vast array of functions, from thinking and feeling to controlling movement and regulating bodily functions. Different regions of the brain specialize in different tasks. For example, the cerebral cortex is responsible for higher-level cognitive functions, while the brainstem controls basic life functions like breathing and heart rate. [Link to Brain Anatomy Article]
- The Spinal Cord: The spinal cord acts as a highway, transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It also plays a role in reflexes, allowing for rapid responses to stimuli.
The CNS processes information, makes decisions, and sends instructions to the rest of the body.
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): The Communication Network
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is the network of nerves that extends from the CNS to the rest of the body. It acts as a communication network, relaying sensory information from the body to the CNS and carrying motor commands from the CNS to muscles and glands.
The PNS is divided into two main divisions:
- The Somatic Nervous System: This system controls voluntary movements, such as walking and talking. It transmits signals to skeletal muscles.
- The Autonomic Nervous System: This system regulates involuntary functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It’s further divided into:
- The Sympathetic Nervous System: The “fight-or-flight” response, preparing the body for stress.
- The Parasympathetic Nervous System: The “rest-and-digest” response, conserving energy and promoting relaxation.
The Synapse: Where Neurons Connect
Neurons don’t physically touch each other; instead, they communicate across a tiny gap called the synapse. This is where the magic of communication happens!
The Synaptic Process:
- Action Potential Arrival: The action potential reaches the axon terminal.
- Neurotransmitter Release: The arrival of the action potential triggers the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters from the axon terminal.
- Neurotransmitter Binding: Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptors on the dendrites of the receiving neuron.
- Signal Transmission: This binding either excites (making the receiving neuron more likely to fire) or inhibits (making it less likely to fire) the receiving neuron, continuing the signal.
This process is incredibly complex and involves a wide variety of neurotransmitters, each with its specific function. For instance, serotonin plays a role in mood regulation, while dopamine is involved in reward and motivation. [Link to Neurotransmitter Article]
Real-World Applications and Examples
Understanding the nervous system has profound implications in many fields:
- Medicine: Understanding the nervous system is crucial for treating neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke.
- Psychology: The nervous system is the foundation of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Psychologists use this knowledge to treat mental health conditions.
- Education: Knowing how the brain learns can help educators create more effective teaching strategies.
Case Study: Consider a person touching a hot stove. Sensory receptors in the skin detect the heat and send signals through the PNS to the spinal cord (CNS). The spinal cord quickly initiates a reflex arc, causing the person to withdraw their hand before the brain even consciously registers the pain. The brain then receives the signal, allowing the person to understand what happened and learn from the experience.
Conclusion: Your Brain’s Power Unleashed
The nervous system is a marvel of biological engineering, and understanding its basic components – the neuron, CNS, PNS, and synapse – is the first step toward appreciating its complexity and power. By learning about these fundamental elements, you’re gaining insight into how your brain works, how you think, feel, and interact with the world. Download the nervous system worksheet [Link to Worksheet - hypothetical download] to test your knowledge and continue your journey of discovery. Further research on specific areas of the nervous system, such as the different brain regions or specific neurotransmitters, will deepen your understanding even further. Continue exploring, and you’ll be well on your way to unlocking the secrets of your amazing brain!