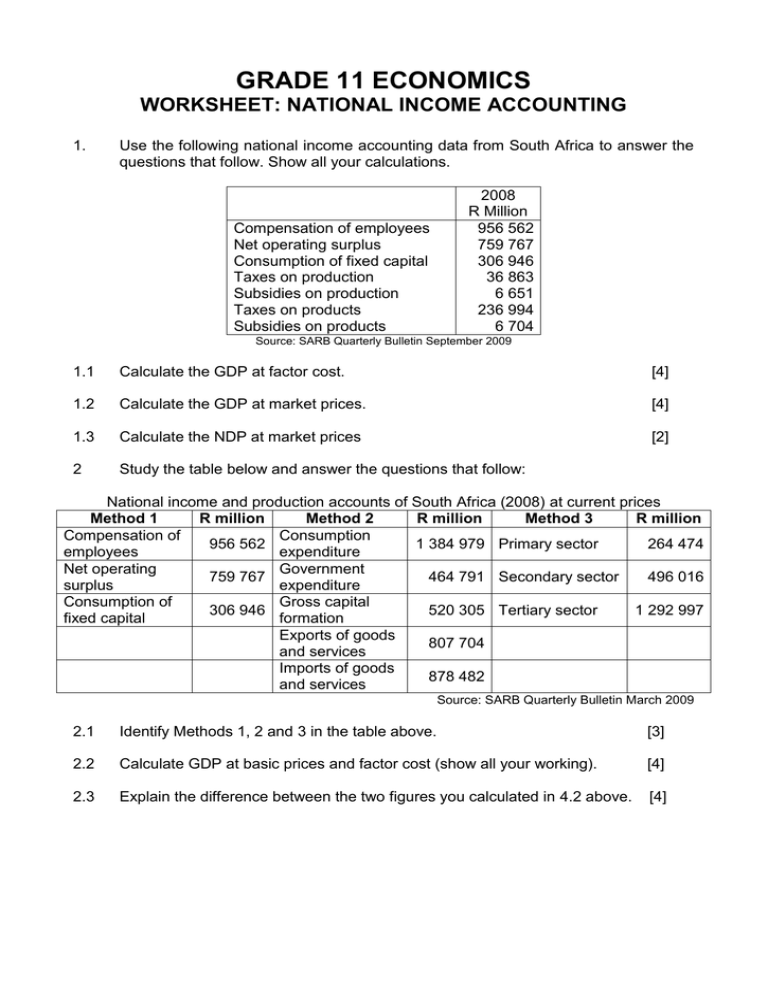
Here’s an article draft meeting all your specifications:
html Unlock Unit 1 Intro to Economics Worksheet Answers: Ace That Quiz NOW! Unlock Unit 1 Intro to Economics Worksheet Answers: Ace That Quiz NOW! Feeling overwhelmed by your Introduction to Economics worksheet? Unit 1 can be a challenging starting point, introducing fundamental concepts that build the foundation for everything else you'll learn. Don't worry! This guide will break down the key topics and provide insights to help you understand the core principles, tackle common questions, and, most importantly, ace that quiz. We'll demystify the jargon and arm you with the knowledge you need to succeed. What's Covered in Unit 1: Introduction to Economics? Unit 1 typically lays the groundwork for your economics journey. You'll encounter essential definitions, explore core economic problems, and begin to understand how societies make choices. Here's a breakdown of common topics: Scarcity: The fundamental economic problem – unlimited wants versus limited resources. Opportunity Cost: The value of the next best alternative forgone when making a choice. Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF): A graphical representation of a society's production choices. Economic Systems: Different ways societies organize their economies (e.g., market, command, mixed). Basic Economic Questions: What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce? Factors of Production: Land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Key Concepts Explained: Demystifying the Basics Scarcity and its Implications Scarcity is the cornerstone of economics. It means that we have unlimited wants but limited resources. This forces us to make choices. Think about it: you might want a new car, a vacation, and a bigger house, but your income is limited. This is scarcity in action. Because of scarcity, we must make choices about how to allocate our resources. This leads directly to the concept of opportunity cost. For more in-depth understanding, see: [Link to a reputable economics website explaining scarcity, e.g., Investopedia, Khan Academy] Understanding Opportunity Cost Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative. When you choose to study for your economics quiz instead of going to a concert, the opportunity cost is the enjoyment you would have gotten from the concert. It’s not just about money; it's about the value of what you give up. A business considering building a new factory must weigh the opportunity cost of that investment against other potential uses of its resources. Understanding opportunity cost helps you make rational decisions. Example: Suppose you have $20. You can either buy a pizza or go to the movies. If you choose the pizza, the opportunity cost is the enjoyment of the movie. If you choose the movie, the opportunity cost is the pizza (and the satisfaction it brings). The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) The PPF is a crucial tool for understanding economic choices. It's a graph that shows the various combinations of goods and services that a society can produce given its available resources and technology. Points *on* the PPF represent efficient production (using all resources), points *inside* the PPF represent inefficient production (resources are not fully used), and points *outside* the PPF are unattainable with current resources. A shift in the PPF (outward or inward) indicates economic growth or decline, respectively. Economic growth can occur due to technological advancements or an increase in resources, such as more labor or capital. For visual explanations, search on YouTube: [Link to a YouTube video explaining PPF with diagrams] Common Worksheet Questions and How to Answer Them Worksheet questions often test your understanding of the core concepts. Here are some common question types and how to approach them: Define Scarcity: Explain the fundamental economic problem of limited resources and unlimited wants. Explain Opportunity Cost: Clearly state the value of the next best alternative forgone. Give examples. Draw a PPF: Practice drawing and labeling a PPF, showing efficient, inefficient, and unattainable points. Be prepared to explain what a shift in the PPF means. List the Factors of Production: Remember land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Describe Different Economic Systems: Understand the key characteristics of market, command, and mixed economies. Example Question: "If a country chooses to produce more capital goods, what is a likely consequence in the future?" Answer: The country's production possibilities frontier will likely shift outward in the future, leading to economic growth. This is because capital goods (e.g., machinery, factories) increase productivity. Preparing for Your Quiz: Study Strategies Effective study habits are crucial for success. Here's how to prepare: Review Your Notes: Go through your class notes and highlight key definitions and concepts. Practice Problems: Work through practice problems and examples related to each topic. Use Flashcards: Create flashcards to memorize key terms and definitions. Form a Study Group: Discussing concepts with others can deepen your understanding. Seek Clarification: If you're struggling with a concept, ask your teacher or professor for help. Real-World Application: Economics in Everyday Life Economics isn't just a theoretical subject; it affects your daily life. Consider these examples: Making Purchasing Decisions: Every time you choose to buy something, you're making an economic decision, weighing the benefits against the opportunity cost. Choosing a Career: Your career choice involves analyzing the labor market, considering potential income, and assessing the opportunity cost of different career paths. Understanding News Events: Economic news, such as inflation, interest rates, and unemployment, directly impacts your financial well-being and your understanding of the world. Case Study: The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically illustrated economic principles. Supply chain disruptions (scarcity), government stimulus (economic system intervention), and shifts in consumer behavior (market forces) all played significant roles. Conclusion: Ace That Quiz! Mastering Unit 1 Introduction to Economics is the first step toward a deeper understanding of how the world works. By understanding concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, and the production possibilities frontier, you'll be well-equipped to answer those worksheet questions and ace your quiz. Remember to review your notes, practice problems, and seek help when needed. Good luck with your studies – you've got this! For further study, consider exploring these topics: [Link to a reputable economics website with more advanced economics topics].