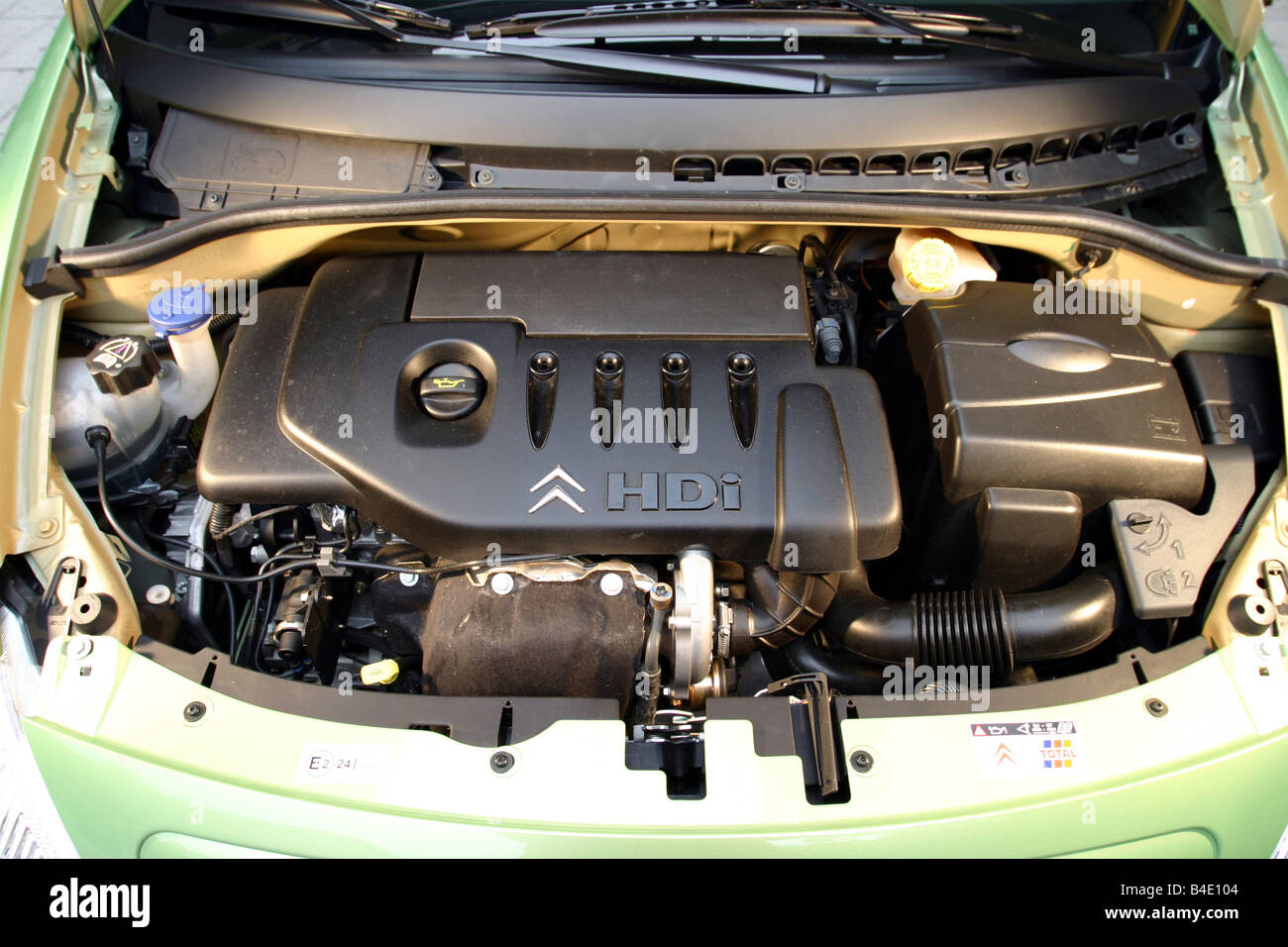
Citroen 1.4 HDi Engine Secrets: Don’t Buy One Until You Read This! - An Introduction
So, you’re considering buying a Citroen with a 1.4 HDi engine? Perhaps you’re drawn to its reputation for fuel efficiency, its compact size, or its affordability. You’re not alone! This engine, found in a wide range of Citroen models and even in vehicles from other brands, has been a popular choice for drivers seeking economical motoring. But before you sign on the dotted line, before you experience the tempting promise of low running costs, you need to arm yourself with vital information. This is because the 1.4 HDi, while offering undeniable advantages, harbors a few secrets – secrets that can significantly impact your ownership experience and, in some cases, your wallet.
This article, “Citroen 1.4 HDi Engine Secrets: Don’t Buy One Until You Read This!”, is your essential guide. It’s designed to equip you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision, protecting you from potential pitfalls and helping you navigate the world of the 1.4 HDi with confidence.
Why is this important?
The 1.4 HDi, like any engine, has its strengths and weaknesses. However, some of its weaknesses are particularly prevalent and can lead to costly repairs if ignored. Ignoring these potential issues can transform the dream of economical motoring into a nightmare of constant maintenance and unexpected bills. This guide aims to:
- Educate you on the common problems: We’ll delve deep into the typical issues that plague the 1.4 HDi, from injector failures to turbocharger woes, and everything in between.
- Help you identify warning signs: We’ll teach you how to recognize the early indicators of potential problems, giving you the power to address issues before they escalate and become expensive.
- Provide practical advice: We’ll offer tips on preventative maintenance, best practices for ownership, and what to look for when buying a used 1.4 HDi.
- Empower you to make an informed decision: Ultimately, our goal is to give you the tools to decide whether a 1.4 HDi is the right engine for you, based on a realistic understanding of its strengths and weaknesses.
Background Context: A Brief History of the 1.4 HDi
The 1.4 HDi (High-pressure Direct injection) engine, also known as the 1.4 Litre diesel, is a product of a collaboration between PSA Peugeot Citroen (now Stellantis) and Ford Motor Company. It was a cornerstone of the “DV” engine family, designed to be compact, fuel-efficient, and suitable for a wide range of vehicles.
- Development: This engine was developed with a focus on minimizing emissions and maximizing fuel economy, meeting the increasingly stringent environmental regulations of the time.
- Applications: The 1.4 HDi found its way into a vast array of Citroen models, including the C1, C2, C3, C4, Berlingo, and Xsara Picasso. It was also used in various Peugeot models, as well as in some Ford, Mazda, and Volvo vehicles.
- Evolution: Over its lifespan, the 1.4 HDi saw various revisions and improvements, including updates to its fuel injection system, turbocharger design, and emissions control technology. However, despite these advancements, certain inherent weaknesses remained.
What to Expect in This Guide:
This article will systematically break down the key areas of concern surrounding the 1.4 HDi engine. We’ll explore topics such as:
- Fuel System Issues: From injector problems to fuel pump failures, we’ll dissect the common fuel system woes.
- Turbocharger Concerns: Understanding the turbocharger’s role and the pitfalls that can arise.
- EGR Valve Problems: The impact of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve on engine performance and reliability.
- Deterioration of Engine Components: Learn about potential wear and tear on key parts like the crankshaft and timing chain.
- Preventative Maintenance: Crucial maintenance tips to keep your 1.4 HDi running smoothly.
- Buying a Used 1.4 HDi: Essential checks and considerations before purchasing a vehicle with this engine.
Get ready to unlock the secrets of the Citroen 1.4 HDi engine. Knowledge is power, and in this case, it could save you a significant amount of money and frustration. Let’s begin!
Citroen 1.4 HDi Engine Secrets: Don’t Buy One Until You Read This! - A Deep Dive
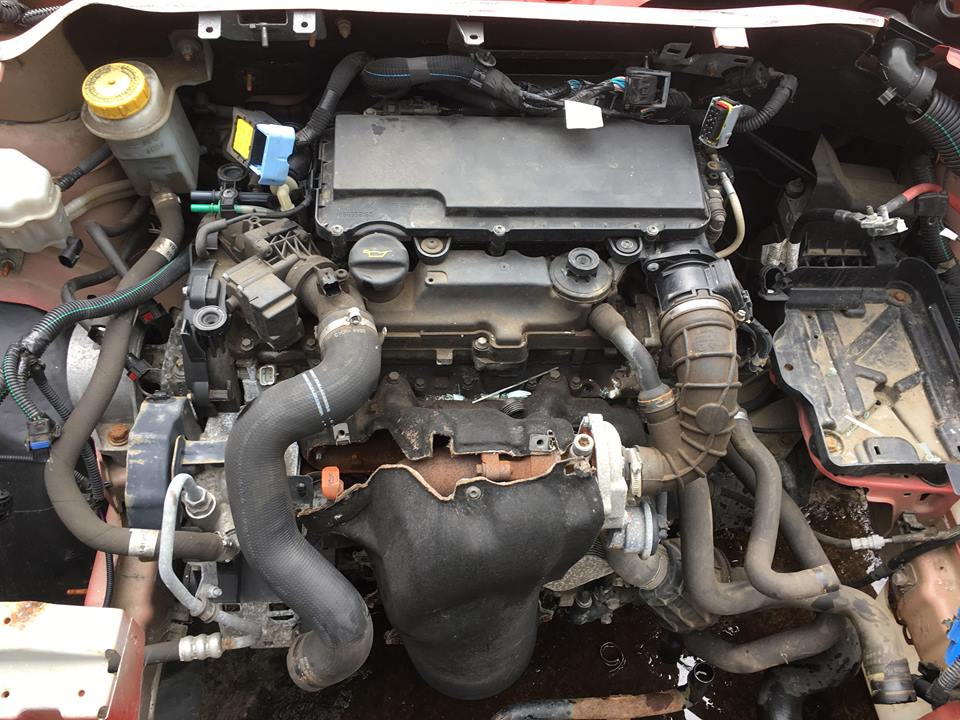
The Citroen 1.4 HDi, also known as the 1.4 Liter High-pressure Direct injection diesel engine, was a popular powerplant found in various Peugeot and Citroen vehicles, and even some other brands like Ford and Mazda. While offering attractive fuel economy and a compact size, it also came with its fair share of quirks and potential pitfalls. This detailed guide will delve into the engine’s secrets, providing you with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision before purchasing a vehicle equipped with this engine.
Key Concepts and Processes:
High-Pressure Direct Injection (HDi): This is the defining feature of the engine. The HDi system injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber under extremely high pressure (up to 1,600 bar or more). This allows for:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Precise fuel metering and atomization lead to more complete combustion, minimizing wasted fuel.
- Reduced Emissions: Better combustion produces fewer harmful pollutants like particulate matter and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
- Increased Power and Torque: The high-pressure system allows for more fuel to be injected during the combustion cycle, leading to better performance.
Diesel Engine Fundamentals: Understanding how a diesel engine works is crucial. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines rely on compression ignition. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Intake: Air is drawn into the cylinder.
- Compression: The piston compresses the air, significantly increasing its temperature.
- Injection: Highly pressurized diesel fuel is injected into the hot, compressed air.
- Combustion: The fuel ignites spontaneously due to the high temperature, driving the piston down.
- Exhaust: The burnt gases are expelled.
Common Rail Fuel System: The 1.4 HDi utilizes a common rail fuel system. This system consists of several key components:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the diesel fuel.
- Fuel Pump (Low-Pressure): Delivers fuel from the tank to the high-pressure fuel pump.
- High-Pressure Fuel Pump (CP1): Pressurizes the fuel to the extremely high levels required for injection. This pump is often driven by the timing belt.
- Fuel Rail: A common rail that stores the pressurized fuel and distributes it to the injectors.
- Fuel Injectors: Precise nozzles that spray the fuel into the combustion chamber. These are controlled electronically by the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): The “brain” of the engine, controlling fuel injection timing, duration, and other parameters to optimize performance and emissions.
- Fuel Filter: Crucial for protecting the sensitive high-pressure components from contaminants.
Turbocharger (Variable Geometry Turbo - VGT): Many 1.4 HDi engines are equipped with a turbocharger, further boosting power and efficiency. Some variants, like those found in later models, feature a Variable Geometry Turbo (VGT). This system uses adjustable vanes to optimize the airflow to the turbine based on engine speed and load, providing better performance across a wider RPM range.
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF): To meet increasingly stringent emissions regulations, many 1.4 HDi engines are equipped with a DPF. This filter traps soot particles from the exhaust gases, reducing particulate emissions. The DPF needs to be periodically “regenerated,” where the trapped soot is burned off.
Potential Problems and Hidden Dangers:
While the 1.4 HDi offers benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential issues:
Timing Belt Failure: This is a critical concern. The timing belt drives the high-pressure fuel pump. Failure of the timing belt results in catastrophic engine damage (bent valves, damaged pistons, etc.). Regular, meticulous timing belt replacement is absolutely essential. The recommended interval is usually between 60,000-80,000 miles (or 5-7 years, whichever comes first), but always consult the manufacturer’s service schedule for the specific vehicle. Ignoring this can be an incredibly expensive mistake.
- Example: Imagine the timing belt snaps while driving at 60 mph. The engine’s timing is lost, and the pistons collide with the valves, causing severe damage. The repair cost can easily exceed the vehicle’s value.
High-Pressure Fuel Pump Failure: The high-pressure fuel pump can be susceptible to wear and tear, especially if the fuel is contaminated. Symptoms of failure include:
Difficulty Starting: The engine might crank but not start, or take a long time to start.
Loss of Power: The engine may lack its usual acceleration and performance.
Rough Running: The engine might run unevenly or misfire.
Fuel Leaks: Visible fuel leaks around the pump are a clear indication of a problem.
Metallic Debris in Fuel System: Pump failure can shed metal particles, which can contaminate the injectors and other components.
Example: A faulty high-pressure pump might cause the engine to stall at traffic lights, leaving you stranded.
Fuel Injector Problems: Fuel injectors are highly sensitive and can be affected by:
- Contaminated Fuel: Debris in the fuel can clog the injectors.
- Carbon Buildup: Over time, carbon can accumulate on the injector nozzles, affecting fuel spray patterns.
- Wear and Tear: Injectors are subjected to extreme pressure and heat, leading to eventual failure.
Symptoms of injector problems include:
Rough Idle: The engine might vibrate or run unevenly at idle.
Misfires: The engine might misfire, causing a loss of power and a rough running condition.
Black Smoke: Excess fuel being injected can lead to black smoke from the exhaust.
Poor Fuel Economy: Faulty injectors can lead to inefficient combustion and reduced fuel economy.
Example: A clogged injector might cause a cylinder to misfire, leading to a noticeable loss of power when accelerating.
Turbocharger Failure: Turbochargers are subject to extreme temperatures and stress. Potential issues include:
- Oil Starvation: Insufficient oil supply can damage the turbo’s bearings.
- Oil Leaks: Leaking oil can contaminate the intake and exhaust systems.
- Wear and Tear: The turbo impeller can wear out over time.
Symptoms of turbocharger problems include:
Loss of Power: The engine might lack its usual acceleration and boost.
Excessive Smoke: Blue smoke (burning oil) or black smoke (overfueling) can indicate turbo problems.
Whining Noise: A high-pitched whining noise can indicate bearing wear.
Oil Consumption: The engine might consume excessive oil.
Example: A failing turbo might cause the engine to feel sluggish and slow to accelerate, especially at higher speeds.
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Issues: DPFs can become clogged with soot, especially if the vehicle is used primarily for short trips or stop-and-go driving, which doesn’t allow the DPF to regenerate properly. Potential issues include:
- Clogging: Reduced exhaust flow and decreased engine performance.
- Regeneration Failure: The DPF might not regenerate correctly, leading to a clogged filter.
- Ash Accumulation: Over time, the ash from the burned soot builds up in the DPF, eventually requiring replacement.
Symptoms of DPF problems include:
Reduced Power: The engine might feel sluggish.
Increased Fuel Consumption: The engine might consume more fuel.
Warning Lights: The DPF warning light or engine warning light might illuminate on the dashboard.
Limp Mode: The ECU might put the engine into limp mode to protect it from further damage.
Example: If you primarily use the vehicle for short trips, the DPF might clog, causing the engine to lose power and potentially triggering a warning light.
EGR Valve (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) Problems: The EGR valve recirculates exhaust gases back into the intake to reduce NOx emissions. These valves can become clogged with carbon deposits, leading to:
Rough Idle: The engine might vibrate or run unevenly at idle.
Stalling: The engine might stall, especially when cold.
Loss of Power: The engine might lack its usual acceleration and performance.
Check Engine Light: The engine warning light might illuminate on the dashboard.
Example: A clogged EGR valve can cause the engine to stall at stoplights.
Dual-Mass Flywheel (DMF) Issues: Some 1.4 HDi engines are equipped with a DMF. The DMF helps to absorb vibrations from the engine, providing a smoother driving experience. DMFs can fail over time, leading to:
Clutch Problems: Difficulties with gear changes, clutch slippage.
Rattling Noises: Noises coming from the bellhousing area.
Vibrations: Excessive vibrations, especially at idle or when accelerating.
Example: A failing DMF can make changing gears difficult and produce a rattling sound when the engine is idling.
Benefits of the 1.4 HDi Engine:
Despite the potential drawbacks, the 1.4 HDi offers several advantages:
- Excellent Fuel Economy: The engine is renowned for its fuel efficiency, making it a cost-effective choice for daily driving.
- Compact Size: The small size makes it suitable for compact cars, contributing to maneuverability and agility.
- Relatively Low Emissions (when functioning correctly): The HDi system helps to reduce harmful emissions compared to older diesel engines.
- Good Performance for its Size: The turbocharger provides decent power and torque for everyday driving.
Important Details to Consider Before Buying:
- Service History is King: Always insist on seeing a complete service history. This is the most crucial factor. Verify that the timing belt has been replaced at the recommended intervals. Look for evidence of regular oil changes, fuel filter replacements, and any other maintenance performed. A well-maintained engine is significantly less likely to suffer from major problems.
- Pre-Purchase Inspection (PPI): Get a professional pre-purchase inspection (PPI) from a reputable mechanic. This is a worthwhile investment. The mechanic can identify potential problems, assess the engine’s condition, and provide a detailed report. This will help you avoid buying a lemon. The PPI should include:
- Compression test: Assesses the condition of the cylinders.
- Fuel system inspection: Checks for leaks, contamination, and injector performance.
- Turbocharger inspection: Checks for leaks, wear, and proper operation.
- DPF inspection: Checks for clogs or signs of problems.
- EGR valve inspection: Checks for proper function.
- Timing belt inspection (if possible): Visually inspect the belt for wear and tear, but remember a full inspection requires removal of covers.
- Test Drive: Thoroughly test drive the vehicle. Pay attention to:
- Starting: Does the engine start easily and quickly?
- Idle: Does the engine idle smoothly or rough?
- Acceleration: Does the engine accelerate smoothly, or does it feel sluggish or hesitate?
- Smoke: Look for any unusual smoke from the exhaust (black, blue, white).
- Warning Lights: Check for any warning lights on the dashboard.
- Noises: Listen for any unusual noises (rattling, whining, knocking).
- Fuel Quality: Use high-quality diesel fuel. This can help prevent fuel system problems. Avoid using fuel from unreliable sources.
- Driving Habits: Avoid short trips and stop-and-go driving if possible. These driving conditions can increase the risk of DPF problems. If your driving primarily consists of short trips, consider a gasoline engine.
- DPF Regeneration: If the DPF warning light illuminates, take the vehicle for a long drive at highway speeds (above 40 mph) to allow the DPF to regenerate. This will help clear the filter.
- Oil Changes: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals. Use the correct type of oil as specified in the owner’s manual. Regular oil changes are crucial for engine longevity.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace the fuel filter at the recommended intervals. A clean fuel filter is essential for protecting the high-pressure fuel system components.
- Research Specific Model Variants: Research the specific model year and trim level of the vehicle you are considering. Some variants of the 1.4 HDi engine might have specific known issues. Online forums and owner groups can be valuable resources for this information.
Conclusion:
The Citroen 1.4 HDi engine can be a good choice for those seeking excellent fuel economy and a compact diesel engine. However, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential problems and to take precautions to minimize the risks. Thorough research, a meticulous service history, a pre-purchase inspection, and a careful test drive are essential before buying a vehicle equipped with this engine. By following these guidelines, you can increase your chances of owning a reliable and efficient vehicle. Ignoring these crucial steps could lead to costly repairs and significant headaches. Be informed, be prepared, and make a wise decision.
Citroen 1.4 HDi Engine Secrets: Don’t Buy One Until You Read This! - FAQ
This FAQ aims to provide comprehensive information about the Citroen 1.4 HDi engine, addressing common concerns, practical considerations, and debunking misconceptions. This is a guide to help you make an informed decision before purchasing a vehicle equipped with this engine.
General Questions:
1. What is the Citroen 1.4 HDi engine?
The 1.4 HDi (High-pressure Direct Injection) engine is a small, four-cylinder diesel engine developed by PSA Peugeot Citroën (now Stellantis). It’s known for its fuel efficiency and was widely used in various Citroen models, primarily focusing on entry-level and city cars.
2. Which Citroen models commonly feature the 1.4 HDi engine?
The 1.4 HDi was prevalent in several Citroen models, including:
- C2
- C3 (first and second generations)
- Berlingo (first and second generations)
- Xsara (early models)
- Saxo (very early models - a variant of the HDi)
3. What are the main advantages of the 1.4 HDi engine?
The primary advantages of the 1.4 HDi are:
- Excellent Fuel Economy: Known for its impressive miles per gallon (MPG), making it a cost-effective choice for fuel consumption.
- Relatively Low Running Costs: Besides fuel, it can also have lower road tax costs in some regions.
- Compact Size: This allows it to fit into smaller vehicles, making them agile and easier to maneuver.
- Availability of Parts: Parts are generally readily available and relatively inexpensive.
4. What are the main disadvantages of the 1.4 HDi engine?
The primary disadvantages are:
- Performance: The engine is not known for its powerful acceleration, making it less suitable for high-speed driving or heavy loads.
- Durability Concerns: Certain components can be prone to failure, potentially leading to costly repairs.
- Potential for Expensive Repairs: While parts are generally cheap, certain failures, such as turbocharger issues, can be costly.
- Noise and Vibration: Diesel engines can be noisier and vibrate more than their petrol counterparts, especially at idle.
5. Is the 1.4 HDi a reliable engine?
Reliability is a mixed bag. While some owners experience trouble-free ownership, the 1.4 HDi has known weaknesses. Regular maintenance is crucial for maximizing its reliability.
Specific Issues and Concerns:
6. What are the most common problems with the 1.4 HDi engine?
Common problems include:
- Turbocharger Failure: A frequent issue, often caused by oil starvation or blocked oil feed pipes.
- Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF) Failure: More common in later models, leading to clutch slippage and noise.
- EGR Valve Issues: The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve can become clogged with soot, leading to performance problems and potential limp mode.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Injectors can fail over time, causing rough running, poor starting, and increased fuel consumption.
- Oil Leaks: Various seals and gaskets can leak, potentially causing engine damage if the oil level drops too low.
- Glow Plug Failure: Difficult starting in cold weather can be a symptom of glow plug failure.
7. How can I prevent turbocharger failure?
- Regular Oil Changes: Use high-quality, correctly specified oil and change it at the recommended intervals or even more frequently (e.g., every 6,000-8,000 miles).
- Warm-up and Cool-down: Allow the engine to warm up before driving hard and cool down after spirited driving.
- Check Oil Feed Pipes: Regularly inspect the oil feed and return pipes for any blockages or restrictions.
- Avoid Prolonged Idling: Excessive idling can reduce oil pressure and contribute to turbocharger damage.
8. What should I do if the EGR valve fails?
- Diagnosis: Get the fault diagnosed by a qualified mechanic.
- Cleaning or Replacement: The EGR valve can sometimes be cleaned, but replacement is often the best solution, especially if it’s severely clogged or damaged.
- Consider Blanking (with caution): In some regions where it’s legal, blanking the EGR valve can prevent future issues, but this can affect emissions and may not be legal in all areas. Consult a mechanic about the legalities and potential drawbacks.
9. What are the signs of a failing Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF)?
- Rattling Noise: A rattling or knocking noise, especially at idle or during gear changes.
- Clutch Slippage: The engine revs increase without a corresponding increase in speed.
- Vibration through the Clutch Pedal: A noticeable vibration when pressing the clutch pedal.
- Difficulty Selecting Gears: Problems shifting gears smoothly.
10. How much does it cost to replace a turbocharger?
The cost of replacing a turbocharger can vary significantly, depending on the location, the type of turbocharger (new, reconditioned), and labour costs. Expect to pay between £400-£1000+ (or the equivalent in your currency) for a replacement, including parts and labour.
11. How much does it cost to replace a Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF)?
Replacing a DMF is a substantial repair. Costs can range from £600-£1500+ (or the equivalent in your currency), including the flywheel, clutch, and labour.
12. How can I tell if the fuel injectors are failing?
- Rough Running: The engine may run unevenly or misfire.
- Difficulty Starting: Hard starting, especially when cold.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A noticeable drop in fuel economy.
- Black Smoke: Excessive black smoke from the exhaust.
- Engine Knocking: Unusual noises from the engine.
13. Is it worth buying a 1.4 HDi car if it has high mileage?
It depends. A well-maintained 1.4 HDi can last a long time. However, high mileage increases the likelihood of component failures. Thoroughly inspect the vehicle, check service history, and consider a pre-purchase inspection by a qualified mechanic. Factor in the potential cost of future repairs when making your decision.
14. Does the 1.4 HDi have a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)?
Some later models of the 1.4 HDi were equipped with a DPF. Check the vehicle’s specifications or consult a mechanic to confirm if the specific model you are considering has a DPF. DPFs require specific maintenance and can be a source of problems if not properly looked after.
15. What are the best ways to maintain a 1.4 HDi engine?
- Regular Oil Changes: Use high-quality, correctly specified oil and change it frequently.
- Use Quality Fuel: Opt for reputable fuel stations and avoid using low-quality fuel.
- Regular Servicing: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals.
- Monitor Coolant Level: Ensure the coolant level is maintained to prevent overheating.
- Inspect for Leaks: Regularly check for oil, coolant, and fuel leaks.
- Address Issues Promptly: Don’t ignore warning lights or unusual noises. Get the vehicle checked by a mechanic as soon as possible.
16. What are the common misconceptions about the 1.4 HDi?
- “It’s Bulletproof”: While fuel-efficient, it’s not necessarily bulletproof. Regular maintenance is crucial.
- “It’s Always Cheap to Repair”: While some parts are inexpensive, major repairs like turbocharger or DMF replacement can be costly.
- “Fuel Economy is Guaranteed”: Fuel economy is excellent, but it can be affected by driving style, maintenance, and vehicle condition.
- “It’s a Powerful Engine”: It’s a small engine; performance is not its forte.
17. Should I buy a Citroen with a 1.4 HDi engine?
This depends on your needs and priorities. If you prioritize fuel economy and low running costs, and are prepared to address potential maintenance issues, it could be a good choice. However, if you require powerful performance or are averse to potential repair costs, you might want to consider a different engine or vehicle. Thoroughly research the specific model you are considering, check its service history, and get a pre-purchase inspection.
18. Where can I find more information and help?
- Online Forums: Search for dedicated Citroen or 1.4 HDi owner forums for advice and support.
- Mechanics: Consult reputable mechanics specializing in Citroen vehicles.
- Vehicle History Checks: Obtain a vehicle history check to uncover any potential problems.
- Owner’s Manual: Refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual for maintenance schedules and specifications.
This FAQ provides a starting point for understanding the Citroen 1.4 HDi engine. Remember to conduct thorough research and consult with qualified professionals before making any decisions. Good luck!
Citroen 1.4 HDi Engine Secrets: Don’t Buy One Until You Read This! - Conclusion & Summary
In this exploration of the Citroen 1.4 HDi engine, we’ve peeled back the layers to reveal both its virtues and its vulnerabilities. From its fuel-efficient nature and nimble performance to its potential for costly repairs and reliability concerns, we’ve aimed to provide a comprehensive overview that empowers you, the potential buyer, with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision.
Recap of Key Points:
- Fuel Efficiency Reigns Supreme: The 1.4 HDi shines with its impressive fuel economy, making it an attractive option for cost-conscious drivers.
- Peppy Performance for Its Size: Despite its small displacement, the engine offers adequate power for city driving and occasional highway use.
- The Dark Side: Reliability Concerns: We’ve highlighted the common issues plaguing this engine, including turbocharger failures, injector problems, oil pump issues, and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) woes.
- Maintenance is Critical: Regular and meticulous maintenance, including timely oil changes with the correct specification oil, is crucial for mitigating potential problems and extending the engine’s lifespan.
- Pre-Purchase Inspection is Non-Negotiable: A thorough inspection by a qualified mechanic, especially focusing on the turbo, injectors, and DPF, is paramount before buying a used 1.4 HDi vehicle.
- Consider the Alternatives: We’ve emphasized the importance of exploring other engine options, especially if reliability and long-term cost are primary concerns.
Final Thoughts:
The Citroen 1.4 HDi engine presents a compelling proposition on paper: fuel efficiency and a decent driving experience in a compact package. However, the reality is often more nuanced. The potential for expensive repairs, coupled with the engine’s sensitivity to maintenance, can quickly erode the initial cost savings. While well-maintained examples can offer years of reliable service, the risk of encountering significant issues is undeniably present.
Actionable Takeaways:
- Prioritize a Comprehensive Pre-Purchase Inspection: This is the single most crucial step. Don’t skip it!
- Demand Service History: Verify the vehicle’s maintenance records to assess its care and potential issues.
- Factor in Potential Repair Costs: Budget for potential issues, even if the vehicle appears in good condition.
- Research Specific Model Years: Some production runs may be more prone to certain problems; research the specific year you’re considering.
- Consider Extended Warranties: If you’re drawn to the 1.4 HDi, an extended warranty can provide peace of mind and protection against unexpected expenses.
Next Steps:
Armed with this knowledge, you are now better equipped to navigate the complexities of the Citroen 1.4 HDi. Before taking the plunge, we strongly urge you to download our free checklist for inspecting used 1.4 HDi vehicles. This checklist provides a detailed guide to the critical areas you need to focus on during your inspection, helping you make a confident and informed decision. Click the link below to download your checklist and take the first step towards a smart purchase! (Insert link to the checklist here).